COMPRESSION SPRINGS
LARGE OR SMALL, SIMPLE OR COMPLEX – WE’VE GOT YOU COVERED
As a premier custom springs manufacturer, we craft compression springs in a variety of compression types, shapes, and materials to your individual specifications. Allow us to review your specifications and offer you a competitive quote.
Examples range from large suspension springs to small electronic control springs.
CORE VALUES
- .007″ – .750″ wire size
- Various wire materials
- Selection of wire shapes – round, rectangular, & square
- Standard & custom compression spring body shapes
- Secondary processes & finishes
- Engineering assistance with spring designs
YOUR DESIGN, OUR QUALITY
FROM CONCEPT TO DELIVERY
CUSTOM MANUFACTURED TO ENSURE FIT AND FUNCTION FOR YOUR UNIQUE APPLICATION.
RAPID RESPONSE RFQ
Submit an RFQ and MWS will review your specifications. Our team will recommend options to help control costs while retaining quality and precision, noting exceptions, if any, directly on your quote to flag concerns or suggest modifications.
HIGH CARBON WIRE
High carbon spring steels are the most commonly used of all materials. Try to use these materials in preference to others because they are least expensive, readily available, easy worked, and most popular. These materials are not satisfactory for high or low temperatures or for shock or impact loading.
| Material | Method of Manufacture • Chief Uses • Special Properties |
|---|---|
| Hard Drawn ATSM A 227 |
Cold drawn. Average stress applications. Lower cost springs and wire forms. |
|
High Tensile Hard Drawn
ATSM A 679 |
Cold drawn. Higher quality springs and wire forms. |
| Oil Tempered ATSM A 229 |
Cold drawn and heat treated before fabrication. General purpose spring wire |
| Carbon Valve ATSM A 230 |
Cold drawn and heat treated before fabrication. Good surface condition and uniform tensile. |
ALLOY STEEL WIRE
The alloy spring steels have a definite place in the field of spring materials. Try to use these materials, particularly for conditions involving high stress and for applications where shock or impact loading occurs. Alloy spring steels can also withstand higher and lower temperatures than the high-carbon steels and are obtainable in either the annealed or pre-tempered conditions.
| Material | Method of Manufacture • Chief Uses • Special Properties |
|---|---|
| Chrome Vanadium Chrome Vanadium |
Cold drawn and heat treated before fabrication. Used for shock loads and moderately elevated temperatures. |
| Chrome Silicon ASTM A401 |
Cold drawn and heat treated before fabrication. Used for shock loads and moderately elevated temperatures. (Mid-West Spring recommends that Chrome Silicon never be electro-plated.) |
STAINLESS STEEL WIRE
The use of stainless steels has increased considerably in recent years. Several new compositions are now available to withstand corrosion. All of these materials can be used for high temperatures up to 650° F.
| Material | Method of Manufacture • Chief Uses • Special Properties |
|---|---|
| ASI 316 ASTM A313 |
Cold drawn. Heat resistant and better corrosion resistant than 302. Magnetic in spring temper. |
| 17-7 PH ASTM A313 (631) |
Cold drawn & precipitation hardened after fabrication. High strength and general purpose corrosion resistance. Slightly magnetic in spring temper. |
NON-FERROUS ALLOY WIRE
Copper-based alloys are important spring materials because of their good electrical properties combined with their excellent resistance to corrosion. Although these materials are more expensive than the high-carbon and alloy steels, they nevertheless are frequently used in electrical components and in subzero temperatures. All copperbased alloys are drawn to the American wire gage (same as Brown & Sharpe gage) and are magnetic.
| Material | Method of Manufacture • Chief Uses • Special Properties |
|---|---|
| Phosphor Bronze Grade A ASTM B159 |
Cold drawn. Good corrosion resistance and for electrical conductivity. |
| Beryllium Cooper ASTM B197 |
Cold drawn and may be mill hardened before fabrication, good corrosion resistance and electrical conductivity. High physicals. |
| Monel 400 AMS 7233 |
Cold drawn. Good corrosion resistance at moderately elevated temperatures. |
| Monel K500 QQ-N-286 |
Excellent corrosion resistance at moderately elevated temperatures. |
HIGH TEMPERATURE ALLOY WIRE
Nickel-based alloys are especially useful spring materials to combat corrosion and to withstand both elevated and below-zero temperature applications. Their magnetic characteristics are important for such devices as gyroscopes, chronoscopes and indicating instruments. These materials have high electrical resistance and should not be used for conductors of electric current.
| Material | Method of Manufacture • Chief Uses • Special Properties |
|---|---|
| A286 Alloy | Cold drawn & precipitation hardened after fabrication. Good corrosion resistance at elevated temperatures. |
| Inconel 600 QQ-W-390 |
Cold drawn. Good corrosion resistance at elevated temperatures. |
| Iconel 718 | Cold drawn & precipitation hardened after fabrication. Good corrosion resistance at elevated temperatures. |
| Iconel X-750 AMS 5698, 5699 |
Cold drawn & precipitation hardened after fabrication. Good corrosion resistance at elevated temperatures. |
FLAT HIGH-CARBON SPRING STEELS
Flat high-carbon Spring Steels General. Although several types of thin flat strip are available for specific applications in watches, clocks and certain instruments only two types are readily available. These two compositions are used for over 95% of all applications requiring flat high-carbon strip. Although these materials are frequently plated, sections under 0.015 in. having carbon content over 0.85 with hardness over Rockwell C47 are highly susceptible to hydrogen-embrittlement even though special plating and heating operations are employed.
Some important factors to consider when ordering your custom compression springs:
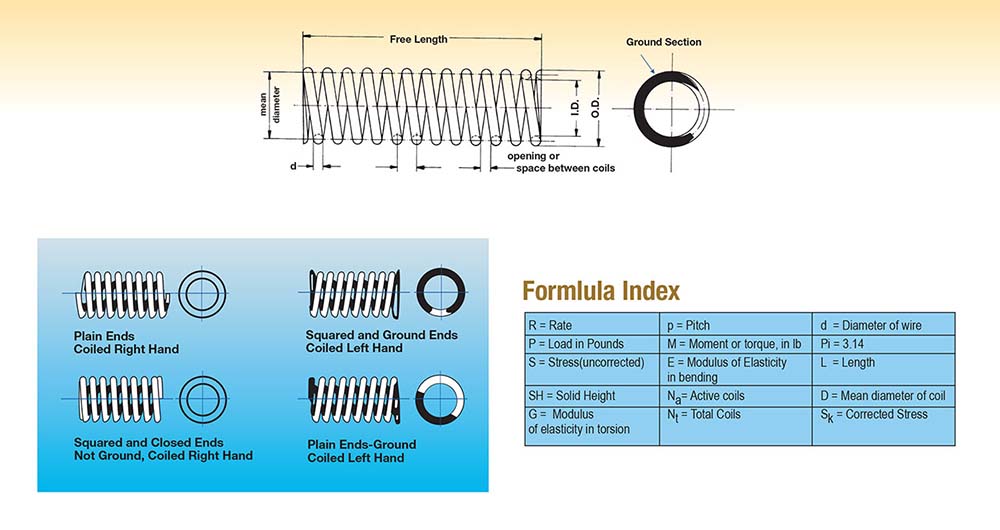
End treatment – Custom springs can have open, open and ground, closed or closed and ground ends.
Free length – How long is the spring when fully extended?
Helix direction – The direction of coils is right or left-handed, depending on how the machine making them is set up. Handedness is important in very few applications.
Load at sold height – The force in pounds required to collapse the spring completely.
Solid height – What is the length of the spring when completely compressed?
Spring rate – How much force in pounds per inch of deflection does it take to compress the spring? See calculating procedure below.
Total number of coils in the spring
Outside diameter of the spring
Wire diameter – Diameters of .007″ to .750″ are available in round, square or rectangular.
Wire material – Custom springs are available in a variety of steel and non-ferrous alloys.
To expedite the RFQ process, choose the option that applies to you:
I have a blueprint or specifications sheet to upload with my request.